Wear means that materials are consumed from their surfaces by mechanical actions, such as friction and grinding, and plating to prevent this wear is called wear-resistant plating. There are two methods of improving the wear resistance: increasing the surface hardness and decreasing the friction coefficient.
| Type of plating | Characteristic value | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial chromium plating | - Hv 800 - 1000 | Bearings of machine parts, crankshafts, piston rods, rolls, molds, inspection tools (block gauges) |
| Microporous chromium plating | - Seizing-up is prevented by using pores for oil retention. | Cylinders of internal combustion engines |
| Teflon-impregnated chromium plating (TEFLOK) | - Non-adhesiveness and low friction coefficient | Various rolls, molds |
| Electroless nickel-phosphorus (5 – 10%P) | - Hv800 – 1000 (heat-treated) Hv500 (not heat-treated) - Electroless plating is suitable for precision machine parts because the plating thickness is uniform in all parts irrespective of product shape. |
Automobiles, aircraft, copiers, etc. |
| Hard noble metal plating | - Noble metal plating with high hardness includes rhodium plating, platinum plating, and ruthenium plating. | Electrical contacts, sliding parts |
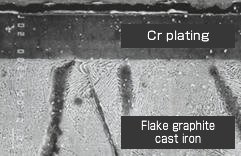
Cross-section SEM photo of hard chromium plating
on flake graphite cast iron