While molten aluminum plating is used to prevent degradation by high-temperature oxidation (400°C) of steel materials, industrial chromium plating and nickel-tungsten alloy plating now play an active part in electroplating.
| Type of plating | Characteristic value | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial chromium plating | - In a high-temperature oxidation atmosphere of 400°C, the hardness drops from Hv1,000 to Hv600. | Waste incinerators, heaters, automotive mufflers, boiler parts, glass molds, etc. |
| Nickel plating and nickel-tungsten alloy plating | - Nickel plating is usable even at high temperatures of approximately 300 – 500°C. - Nickel-tungsten alloy plating is utilized for glass molds subject to continuous use at approximately 600°C. For details, see the illustration below. |
|
| Electroless nickel plating | - Thermal resistance is up to approximately 200°C. Ni-B > Ni-P |
|
| Nickel-cadmium dispersed plating | - Used for aircraft engine bolts requiring thermal resistance and corrosion resistance. | Aircraft parts |
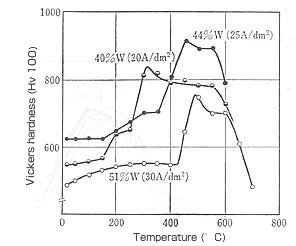
Hot hardness of nickel-tungsten alloy plating