On electrical and electronic parts consisting of many microparts, small contact resistance, and good corrosion resistance, slidability, and wear resistance, etc., are key points for their joints and connections (electrical contacts).
| Type of plating | Characteristic value | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Gold-cobalt alloy plating (0.1 – 1% cobalt) |
- Contact resistance 0.58 – 0.62mΩ - Hv150 – 180 (for contact) - Corrosion resistance as the only non-oxidizing metal - The only disadvantage is that the cost is high. |
Various contacts, switches, contacts |
| Rhodium (Rh) plating | - Hv800~1000 - Low contact resistance - Corrosion resistance and oxidation resistance are as good as being insoluble in qua regia (nitric acid:hydrochloric acid = 1:3) |
|
| Palladium (Pd)-based plating | - Hardness Palladium plating Hv200 – 250 Palladium-nickel alloy plating Hv330 – 380 - Electrical resistance Palladium plating 8.6mΩ Palladium-nickel alloy plating 10mΩ |
|
| Silver plating | - Hv110 – 130 (hard) - Despite excellent electrical conductivity, the only disadvantage is its tendency for discoloration. |
|
| Nickel plating, tin plating | - Used as a substitute for gold plating because the cost is low. - Suitable for needs of approximately 100 or less extractions with maximum contact resistance of approximately 10mΩ because tin plating is soft. Since nickel plating is moderately hard, dull plating and semigloss nickel plating are used. |
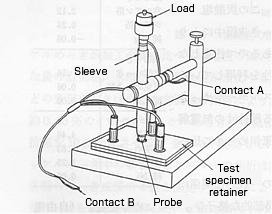
Jig to measure contact resistance
Types of plating