Ceramics can be broadly divided into structural ceramics excelling in thermal resistance, hardness, and corrosion resistance, such as alumina (Al2O3), silicon nitride (Si4N4), and silicon carbide (SiC); and electronic ceramics, such as 2MgO・Al2O3 as insulating materials, BaTiO3 as dielectric materials, PZT(Pb(Zr, Ti)O3) and other piezoelectric materials, and titania (TiO2) and other sensor materials. Tin plating and gold plating are used to form electrodes on IC boards and IC packages.
| Field | Functions and names | Type of ceramic | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light | Optical transfer (glass optical fiber) Modulation and deflection of light (ferroelectric body) Absorptance and reflectance change (optical memory material) Light-energy conversion (photoelectrochemical film) |
Silica-based glass LiNbO3 thin film Chalcogenide-based amorphous film Titanium oxide film |
Optical communication Light passageway, light shutter Laser disk Hydrogen formation from water |
| Electromagnetism | High dielectric constant (dielectric body) High piezoelectric effect (piezoelectric body) High ionic conduction (super-ionic conductor) |
BaTiO3 lead zirconate titanate β-alumina (Al2O3) |
Chip capacitors, PZT spark plugs Solid cells, circuit boards (hybrid ICs, power modules) |
| Heat | Thermal shock resistance (low-expansion ceramic) Low-temperature firing (substrate) |
SiO2-TiO2 glass Crystallized glass |
Astronomical telescopes Circuit boards |
| Mechanical structure | High strength and thermal resistance (high-strength, high-toughness ceramic) Machinability (mica crystallized glass) |
Alumina, stabilized zirconia, silicon carbide, silicon nitride, diamond K2O‐Al2O3‐SiO2‐F crystallized glass |
Automotive engines, pumps, joining (of ceramics and metals: brazing) Abrasive compounds, scissors |
| Chemical | Catalyst carrier (cellular ceramic) | Porous glass | Automotive exhaust treatment |
| Biological | Biological compatibility (artificial bones, artificial teeth) | Alumina (Al2O2), apatite crystal | Joints, teeth, artificial bones |
(From “Sentanzairyo no Kiso-Chishiki” edited by the Society of Materials Science, Japan; Ohmsha)
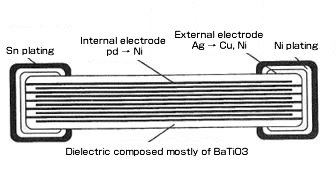
Cross-section structure of laminated ceramic capacitor